Informations on C2A Software
| User Interface | Star Catalogues | Deep Sky Catalogues | Features |
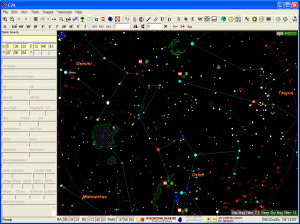
C2A has been designed to answer the following objectives:
- It must be easy to use and should not require the reading of a manual in order to be mastered;
- It must take into account the most usual star catalogues available to amateur and professional astronomers (SAO, GCVS, Guide Star, USNO, Hipparcos, Tycho-2, UCAC2, UCAC3, UCAC4, USNO, ...). For the Tycho-2, Hipparcos and UCAC catalogues, proper motions must be taken into account in order to report object positions which depend on the observation date. So this usage is astrometry and photometry oriented;
- It must take into account the most usual deek sky object catalogues: Messier, NGC, IC and PGC.
- It must allow users to integrate their own object catalogues;
- It must allow users to display images associated to the objects displayed on the screen, in particular the BT Atlas images. This feature can be used for supernovae search in galaxies.
- It must include a tool to manage orbital elements in order to display asteroid and comet paths (with direct access to orbital elements updates through the Web). This function is useful to predict occultations and to perform asteroid search.
- It must provide a very good accuracy regarding planetary positions (astrometric positions which are required to compare the object positions with the sky background). This feature is useful for occultation observations.
- It must include a full ephemeris generator, including objects such as asteroids and comets known through their orbital elements.
User Interface |  |
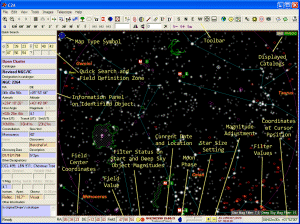 C2A has a simple and user friendly interface. The image on the left describes the main interface elements which are available to the user in the main window of the program.
C2A has a simple and user friendly interface. The image on the left describes the main interface elements which are available to the user in the main window of the program.
A first important thing must be noted in the main window. This is the type of the map which is displayed in the top left corner of the current view. C2A can display two types of map: those with a field type for which the North Celestial pole is by default in the direction of the top of the screen (it is possible to perform rotations and symmetries), and those of type horizon for which the map is oriented in such a way that the closest horizon point is in the direction of the bottom of the screen. In the example on the left, the view has the type field with the North Celestial pole at the top of the screen.
The second important point to be noted is the presence of the two small LEDs in the status bar at the bottom of the main window. They actually display the status of the filters for the stars (left one, which only apply to magnitudes) and deep sky objects (right one, which apply to both magnitude and object type). Green means that there is no filter in action, i.e. all the objects are displayed. Yellow indicates that an automatic filter is currently applied which depends on the zoom level. Finally, red means that a manual filter has been set by the user. A gray LED indicates that there is no catalogue displayed (respectively for stars and deep sky objects).
Identifying an object in the current map can easily be done through a double-click on the object with the mouse left button. To search an object by its name, the user just has to type the string to be searched into the Quick Search zone located at the top left corner of the program window. The search is launched simply by hitting ENTER on the keyboard.
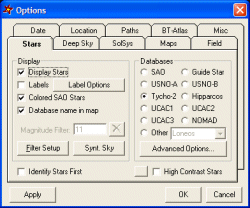 Many options are available to parameterize the views. All these options are gathered into a single dialog box which has several tabs. This option dialog box cand be accessed from the Tools menu or through the keyboard shortcut F7.
Many options are available to parameterize the views. All these options are gathered into a single dialog box which has several tabs. This option dialog box cand be accessed from the Tools menu or through the keyboard shortcut F7.
Some of the options from the dialog box are also directly accessible from the program menu or through keyboard shortcuts, e.g. the display of constellation lines or the database to use in the maps.
The tab Date allows the user to specify the date to be used to compute the map and the tab Location specifies the observation location in latitude and longitude. The tab Paths is also important as it is the way to indicate C2A where its object databases are located, in particular the large star catalogues which are not provided with the standard distribution of C2A and that need to be installed separately on the user's computer.
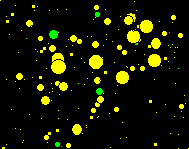
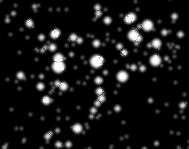 C2A can display stars under the form of colored disks or under the form of synthetic stars that reproduce the aspect of stars that can be obtained on a CCD image.
C2A can display stars under the form of colored disks or under the form of synthetic stars that reproduce the aspect of stars that can be obtained on a CCD image.
Toggling between the two types of display can be done through the option dialog box or simply using the Ctrl+Y keyboard shortcut.
Star Catalogues |  |
C2A is able to read and display objects from several catalogues. The links in the table below give access to snapshots of the same field with the different catalogues which are supported by C2A (only the GCVS, WDS, Loneos, ArasBeAM and Exoplanet Transit Database catalogues are displayed with a larger field where all the Orion constellation is displayed). Using the same field gives an idea of the respective star density for each catalogue. This field is centered on coordinates Alpha=3h38m / Delta=-35°33 and has a 2° width. It includes several bright galaxies which are displayed in all the fields.
In the descriptions below, a color code is used to indicate where each catalogue can be found:
 The catalogue is part of the C2A standard distribution (it is provided in a format specific to C2A)
The catalogue is part of the C2A standard distribution (it is provided in a format specific to C2A)
 The catalogue is optional and must be downloaded from the C2A Web site (it is provided in a format specific to C2A)
The catalogue is optional and must be downloaded from the C2A Web site (it is provided in a format specific to C2A)
 The catalogue must be obtained from the institution which publishes it (it is read by C2A in its native format)
The catalogue must be obtained from the institution which publishes it (it is read by C2A in its native format)
 The catalogue is directly accessed through Internet (it is read by C2A in its native format)
The catalogue is directly accessed through Internet (it is read by C2A in its native format)
 The catalogue must be obtained from the institution which publishes it and must then be compiled to be used by C2A.
The catalogue must be obtained from the institution which publishes it and must then be compiled to be used by C2A.
Red boxes in the catalogue descriptions below provide information about how some key large catalogues (the ones recommended for astrometry) must look like when installed on your local computer hard disk drive. In particular, the exact sizes of some data files are provided in order to validate a catalogue installation on your PC.
SAO Catalogue |
Hipparcos Catalogue |
||
Guide Star Catalogue C2A is also abale to read the versions 1.2 and ACT of the Guide Star catalogue, but these catalogues are not provided with C2A and must be sourced separately.
|
Tycho-2 Catalogue |
||
USNO-SA1.0 and USNO-A2.0 Catalogues |
USNO-B1.0 Catalogue |
||
UCAC1 Catalogue |
UCAC2 Catalogue |
||
UCAC3 Catalogue
|
UCAC4 Catalogue
|
||
NOMAD Catalogue
|
PPMXL Catalogue
|
||
GCVS Catalogue |
WDS Catalogue |
||
Loneos Catalogue |
ArasBeAM Catalogue |
||
Exoplanet Transit Database |
Meteor Shower Catalogue |
||
Asterism Catalogue |
Gliese Catalogue |
||
CMC15 Catalogue |
URAT1 Catalogue
|
Deep Sky Object Catalogues |  |
C2A natively integrates several catalogues of deep sky objects. The table belows provides descriptions of these deep sky object catalogues. The links point to screen snapshots which show these different catalogues in the same field (this field is centered on coordinates Alpha=3h38m / Delta=-35°33 and has a 2° width)./p>
In the descriptions below, a color code is used to indicate where each catalogue can be found:
 The catalogue is part of the C2A standard distribution (it is provided in a format specific to C2A)
The catalogue is part of the C2A standard distribution (it is provided in a format specific to C2A)
 The catalogue itself is provided in the C2A standard distribution but the associated images must be downloaded from the Web site.
The catalogue itself is provided in the C2A standard distribution but the associated images must be downloaded from the Web site.
Revised New General Catalogue and Index Catalogue |
Deep Sky Object Catalogue |
|
PGC Catalogue |
BT-Atlas Catalogue |
|
SAC Catalogue |

In addition to the deep sky object catalogues mentioned above, C2A has the capability to access the images of the Digitized Sky Survey (DSS) from the ESO and STScI and to display these images in a separate window or in the background of the current field. In this version, the access to the DSS is only performed through Internet on the ESO DSS server or STScI server. In order to access these images, your platform must be connected to the Internet.
This screenshot on the right shows a field map (the same as in the examples above but with a field limited to 40 arcminutes) with the ESO DSS image in the background and the object from the Tycho-2 and RNGCIC catalogues in the front-end. We can there is a very good matching between the objects in the image and the objects from the catalogue.
The DSS image download is very easily performed with one mouse click (Ctrl+F8 is a keyboard shortcut) when the field is smaller than 40 arcminutes (in order to limit the size of the download). Once an image is downloaded, it can then be modified and reapplied as the current map background.
Features |  |
C2A includes many features and functions which can be summarized in the table below. Simply click on links to access some screenshots.
| Milky Way display | C2A displays the Milky Way whatever is the zoom level. Bézier curve computing is performed in order to render curved shapes. |
| Nebulae display | When the RNGCIC (Revised New General Catalogue and Index Catalogue) catalogue is the currently displayed catalogue, a certain number of diffuse nebulae are displayed with their real shape. The display of nebulae's shapes depends on both the zoom level and the filters in place for the deep sky objects. Some shapes are directly associated to NGC and IC objects (in which case they are displayed in light green) while others are not related to any specific NGC or IC objects (they can typically include several NGC and IC objects, in which case they are displayed in dark green). |
| Solar System | Regarding the Solar System, positions computing of the Sun, Moon and planets are performed using some special algorithms from the Institut de Mécanique Céleste (Bureau des Longitudes) in Paris. Polynomial coefficients used in these algorithms provide a very high accuracy on object positions (1/100 arc second over the period 1987/2020, which can be extended to 2100 using the polynomial coefficient file available in the Downloads page of this site). The screenshot shows Venus path with a retrogradation at the top of a synthetic sky background. |
| Ecliptic View | C2A integrates a tool to view planet, asteroid and comet positions according to an ecliptic view (accessible from the Tools menu). It is possible to easily change the angle of view as well as the zoom level using the mouse. Furthermore, an animation mode is available. |
| Ephemeris Production | C2A includes a full Ephemeris production system (Moon, Sun, planets as well as comets and asteroids known through their orbital elements). The output step can be adjusted and the produced ephemeris can be saved under the form of a text file or directly printed. |
| Moon Phases | C2A includes a module to compute and display Moon phases for a given month. Furthermore, dates of Full Moon, New Moon, First Quarter and Second Quarter are specifically provided. |
| Asteroids and comets | C2A includes a powerful system to compute asteroid and comet position calculation from their orbital elements. A Graphical User Interface allows the user to import and handle orbital elements. It is possible to import orbital elements directly from the Internet, for instance from the Minor Planet Center site. Several different orbital elements formats are supported. Once the orbital elements are loaded, it is then possible to plot the positions or trajectories of the objects. |
| Planetary Positions | C2A gives the possibility to display planetary positions at 3 different dates for a given month. This display is performed either at the beginning, middle or end of the night. It is done on a map with constant azimut and altitude. This is a useful tool to see at a glance what are going to be the observing conditions for a given object during a given month. It is possible to parameterize the display through numerous options. |
| Proper Motions | C2A is able to take into account proper motions for the stars in the catalogues UCAC1, UCAC2, UCAC3, Hipparcos and Tycho-2. The associated image shows the successive positions of the Barnard's star between 1959 and 2030. This animated image has been created with the UCAC2 catalogue. |
| Image Processing | C2A integrates an image processing tool where the most common tasks around astronomical images can be performed: contrast display, visualization threshold setting, color palette changes, zoom, printing, ... Several different formats are taken into account, either formats with visualization dynamics (FITS, CR2, PPM, PGM and PIC the format of the Iris software), or formats without visualization dynamics (JPG, GIF, BMP). Beside these basics features, C2A has several advanced features: automatic astrometry on a field using the PinPoint engine, image acquisition through the Maxim DL software and a camera focus tool. |
| User Images | The user has the possibility to add its own images in the C2A environment. Once one or several images are associated to a given object (for instance a Messier or an NGC object), access to those images is performed through the button Image... in the information window displayed for that object. The command Image... in the contextual menu can also be used (this menu is displayed with the mouse right button when an object with an associated image is pointed). Object types to which images can be associated to are the following: deep sky objects from the standard deep sky, PGC and RNGCIC catalogues, SAO stars, user objects, Tycho2 star, UCAC1, UCAC2 and UCAC3 stars, ArasBeAM stars, Hipparcos, GCVS, WDS or Loneos stars, planets, Moon, Sun and satellites. User can also associate a text of his/her choice to a given image (for example some comments about how the image was acquired). This text is then automatically displayed in an information box associated to the image. All the images must be stored in a directory declared in the Path tab of the Options dialog box. The first image associated to an object must be named according to the pattern [object name]_1.[extension] where [object name] is the name of the object displayed in the information window and [extension] is the file extension associated to one of the supported image formats (fit, fts, fits, pic, jpg, gif and bmp ). For example, the first JPEG image associated to the object NGC 1972 must be named NGC 1972_1.jpg. The second one must be named NGC 1972_2.jpg, etc... |
| Printing | Maps, ephemeris and pictures can be printed on all the printers supported by the Windows Operating System. Several options are possible to improve printing results as shown in the associated image. To see a printing result in the PDF format, click here. |
| Prepoint Track | C2A includes a simple tool to position a telescope on the sky in such a way that at a given time, a pre-defined object is at the center of the field pointed by the telescope. This function, called prepointing, is especially useful in the scope of occultations of stars by asteroids where, several minutes or hours before the event, the telescope is put in position with the RA tracking stopped. The star will drift in the field of view until it reaches the center at the target time. |
| Telescope Control | C2A offers the possibility to control a telescope through a serial port. By controlling, we mean the following features:
|
| Tracking Drift Analysis | C2A includes a tool to analyze and plot tracking drifts for telescope mountings. In its current version, C2A is able to read data files produced by the Iris software (see Iris web site), Maxim DL, GuideMaster, CCDSoft and AstroArt. C2A offers the user the possibility to "zoom" on some parts of the plot and to copy an image of the plot for future usage. To use this tool, go into the Telescope menu and use the command Tracking Drift Analysis... |
| Focus Tool | C2A includes a tool to help focusing a telescope. This tool is accessible from the Image Processing window once a star has been selected with the mouse. User then simply has to click the Focus button in the tool bar. This tool allows the user to easily see how focus evolves while focus images arrive in a pre-defined directory during the focus process. Focus is plot dynamically through an automatic analysis of the in-coming images. |
| Observation Planning | C2A lets you plan your observations by finding objects meeting a number of criteria. These are the available types of criterion:
Once the objects are identified, they can be highlighted in the maps and the telescope can be automatically pointed towards these objects. |
| Observation Scheduling | C2A includes a tool that lets you put together an observation schedule. It is a list of observations in a certain order that starts at a precise day and time. This tool is different from the Observation Planning tool which is just used to identify objects that meet certain criteria. |
| Planet Visibility | C2A includes a tool that allows you to figure out at a glance what is the visibility during the night of the planets and the moon. Various options are available to customise the display. |
| Sunrise and Sunset | A specific tool let you easily get for a specific date the times for sunrise, sun meridian transit, sunset as well as the times of the Astronomical Twilight (Sun at -18° below the horizon), Nautical Twilight (Sun at -12° below the horizon) and Civil Twilight (Sun at -6° below the horizon). Twilights are provided for both sunrise and sunset. |
Last Update : September 15, 2018 |
[ Version Française ] [ English Version ]